What is Meteorology?
© IMGW
What is Meteorology?
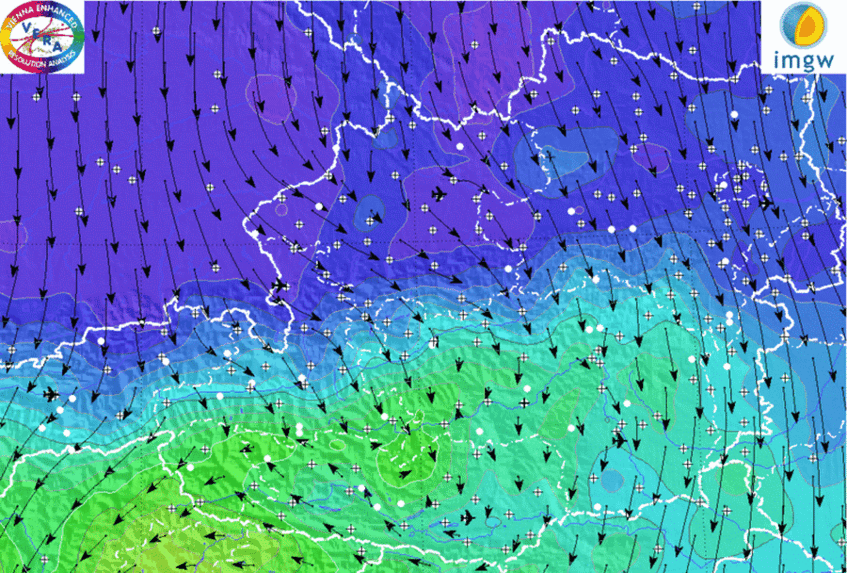
Meteorology applies physical and mathematical methods to understand and forecast the processes that determine our weather. Weather forecasting is a highly complex process in which measurement technology and high performance computing are just as important as the laws of physics and chemistry. For a numerical weather forecast to work, atmospheric data need to be collected, quality controlled and assimilated with suitable integrated weather models. Forecasts are continuously being validated to obtain guidance for further improvements.
Meteorologie und Klima

© IMGW
Meteorologie und Klima
Climatology has been regarded as a subdiscipline of Meteorology for quite some time. Early climate classifications refer to temperature and precipitation as the main factors determining regional climate. Climate parameters such as the occurence of vegetation types, the length of the vegetation period as well as the date of flower blossoms indicate the multidisciplinary character of climatology. Today, climatology or climate research is also referred to as geobiosphere dynamics. It describes the complex interrelations between climate subsystems such as the atmosphere, land, oceans and the biosphere. Despite the considerable growth of the field's scope, meteorology remains central to it, not least because the atmosphere represents the most important transport medium of the climate system.
Meteorologische Forschungsschwerpunkte
© IMGW
Meteorologische Forschungsschwerpunkte
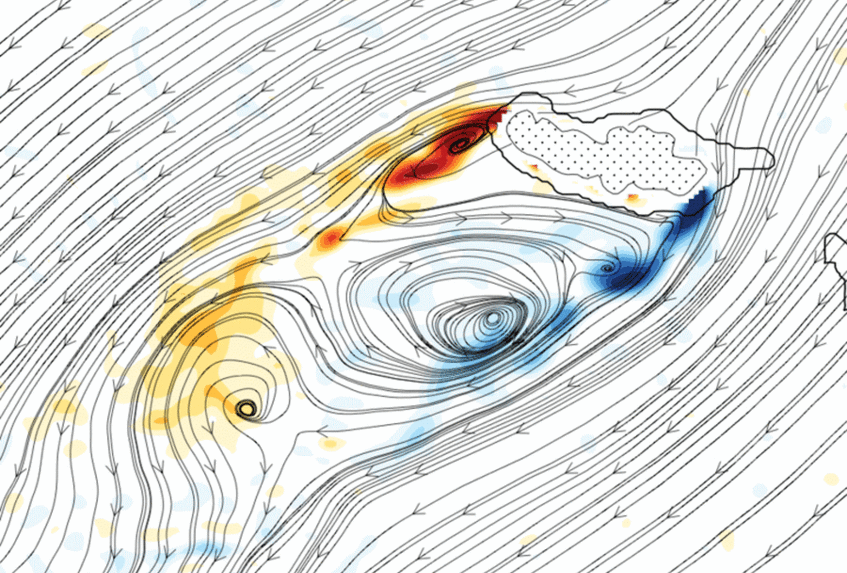
Since its foundation, the Department of Meteorology and Geophysics has been active in mountain meteorology due to its geographical vicinity to the Alps. The activities of the IMGW in this area range from exploration of sink holes, where extremely cold temperatures can develop, to objective analysis over complex terrain and to studies about the change of snow cover duration in a changing climate. Recently, a new research focus on observations and numerical simulations of complex flows over mountains was established.[more]
